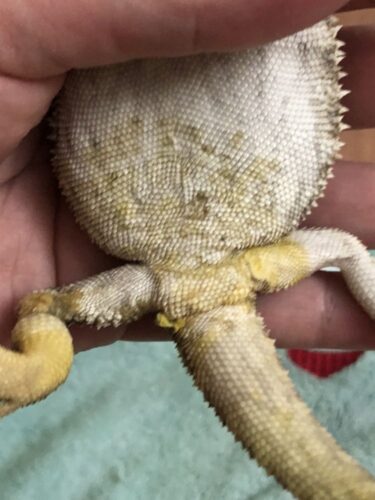
Yellow fungus in bearded dragons is a serious skin infection that can spread rapidly, causing painful lesions and severe health problems. How to treat yellow fungus on bearded dragon is a crucial concern for any owner facing this troubling infection. This
condition can lead to painful skin lesions and serious health complications if not addressed promptly. Timely intervention is essential to ensure your bearded dragon’s well-being and promote a swift recovery.
What is Yellow Fungus in Bearded Dragons

Yellow Fungus Disease (YFD) is a fungal infection that primarily affects reptiles, including bearded dragons. Caused by the fungus Nannizziopsis guarroi, YFD is highly contagious and aggressive, leading to tissue damage and eventually death if untreated.
Common Causes and Risk Factors:
- Poor Husbandry: Unclean or improperly maintained enclosures can harbor fungal spores.
- Weak Immune System: Stress, poor diet, or illness can weaken a bearded dragon’s immune system, making them more susceptible.
- Wounds or Injuries: Open wounds can allow the fungus to enter the skin.
- Humidity and Temperature Issues: Inconsistent humidity or temperature levels can promote fungal growth.
Symptoms to Watch For:
- Yellow Skin Discoloration: Particularly on affected areas, such as limbs, body, or tail.
- Crusty or Scaly Skin: Patches may look dry, flaky, or crusty.
- Sores or Lesions: Open, ulcerated wounds often develop as the infection progresses.
- Loss of Appetite: Bearded dragons may stop eating due to discomfort.
- Lethargy: Affected dragons often become inactive and sluggish.
Early detection and prompt veterinary care are vital to successfully treating yellow fungus disease.
How to Identify Yellow Fungus Disease
Visual Signs:
- Skin Discoloration:
One of the earliest and most noticeable signs of yellow fungus disease (YFD) is a change in skin color. The affected skin will develop yellowish or mustard-colored patches. In some cases, the color may look more brown or grey, but the characteristic yellow hue is a strong indicator. These patches typically start in localized areas, such as the belly, limbs, or tail, but can spread if left untreated. - Rough, Crusty Skin:
As the infection progresses, the patches of discolored skin may become rough or crusty to the touch. The texture becomes dry, flaky, and scaly, giving the skin a coarse appearance. These areas can crack, making the dragon’s skin prone to further damage, and may start shedding abnormally in infected sections. Healthy skin should shed cleanly, but fungal infection can prevent smooth shedding, creating layers of stuck or damaged skin. - Open Lesions or Ulcers:
In more advanced stages, YFD causes the skin to develop open sores or ulcers. These lesions often expose deeper tissue, and they may become infected with bacteria. The affected areas can bleed or ooze fluid, increasing the risk of a secondary infection. Open sores are painful for the bearded dragon, making them more lethargic and reluctant to move.
Behavioral Changes:
- Lethargy:
Bearded dragons with yellow fungus disease often exhibit a significant decrease in activity. They may spend more time hiding or lying still, rather than basking or moving around their enclosure. This lack of energy is partly due to the pain and discomfort caused by the skin lesions, as well as the toll the infection takes on their overall health. - Loss of Appetite:
Another key behavioral sign of YFD is reduced appetite. Bearded dragons suffering from this infection may refuse food, leading to weight loss and poor overall body condition. This happens because the fungus impacts their immune system, causing the dragon to feel weak and unwell, further discouraging eating. Over time, the refusal to eat may result in a skeletal appearance, with visible weight loss in the tail and limbs.
When to Consult a Vet:
It’s essential to seek veterinary help immediately if you notice any combination of the following signs:
- Persistent yellow or discolored patches on the skin.
- Rough or scaly skin that seems abnormal for a shedding cycle.
- Open sores, bleeding, or signs of infection.
- Extreme lethargy or inactivity.
- A bearded dragon refusing food for more than a couple of days.
A reptile veterinarian will typically conduct a thorough examination and may take skin biopsies or fungal cultures to confirm the diagnosis. Early treatment with antifungal medications can help control the spread of the disease and improve the chances of recovery.
Causes of Yellow Fungus in Bearded Dragons

- Poor Hygiene and Habitat Conditions:
Unsanitary enclosures with dirty substrates and old food create an environment for fungal growth, particularly if moisture and mold are present. - Stress and Weakened Immune Systems:
Stress from improper lighting, temperature fluctuations, or overcrowding weakens the immune system, making dragons more susceptible to infections. - Fungal Infections and Spread:
Yellow fungus is caused by Nannizziopsis guarroi, which spreads through contaminated surfaces, direct contact with infected reptiles, or through open wounds. The infection thrives in warm, moist environments.
Maintaining proper hygiene and reducing stress are crucial for prevention.
Steps to Treat Yellow Fungus
Steps to Treat Yellow Fungus in Bearded Dragons:
- Veterinary Diagnosis and Antifungal Treatment:
- Consult a reptile veterinarian for a thorough examination and diagnosis. They may perform skin biopsies or fungal cultures to confirm yellow fungus disease.
- Based on the diagnosis, the vet will prescribe appropriate antifungal treatments.
- Topical and Oral Antifungal Medications:
- Topical Medications: Apply antifungal creams (e.g., itraconazole or voriconazole) directly to the affected areas as directed by the vet.
- Oral Medications: Administer prescribed oral antifungal medications to combat the infection from within.
- Proper Wound Care and Handling Tips:
- Clean the affected areas gently using a reptile-safe antiseptic solution. Avoid causing further irritation.
- Minimize handling to reduce stress; if necessary, wear gloves to prevent spreading spores.
- Ensure the bearded dragon’s habitat is clean, dry, and well-ventilated to promote healing.
Prompt treatment and diligent care are essential for recovery from yellow fungus disease.
Related Post: Do Moth Balls Keep Snakes Away? Myth or Fact?